Kinase linked and related Receptors
How signal is passed inside the cell ???
Signal transduction is a basic process involving the conversion of signal from outside the cell to a functional change within the cell and that occurs through receptors. A cell targeted by particular chemical signal has receptor protein that recognizes the signal molecule. when ligand attach to receptor protein, receptor undergoes a change in shape.
Introduction
Large and heterogenous group of membrane receptors responding mainly to protein mediators (growth factors and cytokines) and hormone (Insulin).
Cell surface receptors recruit activity of protein kinases in 2 general ways.
- Non receptor tyrosine kinases: Receptor lacking self contained kinase function recruit activities of intracellular protein kinase to plasma membrane (Janus Kinase)
- Receptor tyrosine kinases: posses an intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity that is part of receptor protein. Examples include receptor for growth factors (PDGF, EGF, Insulin, etc.)
Structure of Receptor
These receptors are large proteins consisting of a single chain of up to 1000 residues, with a single membrane spanning helical region (Transmembrane domain), associated with large extracellular ligand bonding domain, and an intracellular domain of variable size with amino acid sequence in ATP binding and substrate binding region. these receptors traverse the membrane only once unlike GPCR , they traverse 7 times.
Functions of Tyrosine kinase receptor
Cell proliferation, differentiation, cell survival, growth, cellular metabolism, Inflammation and tissue repair and immune response
Overexpression of EGF-R (Epidermal growth factor- Receptor) found to cause Breast cancer.
Types of Kinase Receptors
- Receptor tyrosine kinase- Phosphorylates specific tyrosine protein
- Tyrosine Kinase associated receptor- associate with intracellular protein that have tyrosine kinase activity
- Receptor like tyrosine phosphatase- remove phosphate group
- Receptor Guanyl cyclase- Directly catalyzes the production of cGMP
- Serine/Threonine kinase and cytokine receptors
- Histidine kinase associated receptors- kinase phosphorylates itself on histidine and then transfers the phosphate to second intracellular signalling protein.
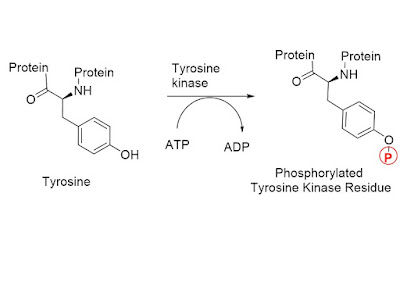
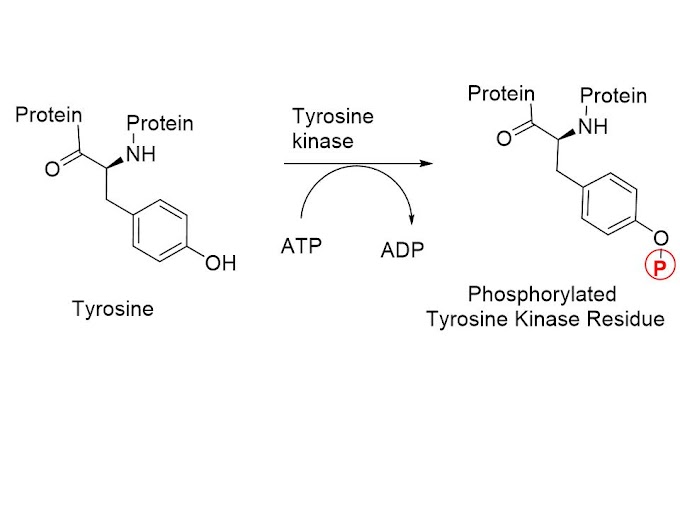
Reaction catalyzed by Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to tyrosine residue in protein. phosphate group is attached to amino acid tyrosine on protein. tyrosine kinase receptor is effective when the cell needs to regulate and coordinate a variety of activities and trigger several signal pathways at once.
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- Intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity
- Soluble or membrane bound ligands :Nerve growth factor (NGF), Platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), Fibroblast growth factor, FGF, Epidermal growth factor (EGF), Insulin,
- Downstream pathway activation : RAS-MAP Kinase pathway




0 Comments